| Sustainability | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › Tourist destination文章 › Sustainability |
Sustainability
|
Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Press
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Notice
clear
Notice
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader. Continue Cancel clearAll articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess. Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications. Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers. Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.  Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Press
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Submit
Journals
Active Journals
Find a Journal
Proceedings Series
Topics
Information
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
Open Access Policy
Institutional Open Access Program
Special Issues Guidelines
Editorial Process
Research and Publication Ethics
Article Processing Charges
Awards
Testimonials
Author Services
Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
About
Overview
Contact
Careers
News
Press
Blog
Sign In / Sign Up
Submit
 5.8
5.8
 3.9
Journals
Sustainability
3.9
Journals
Sustainability
 Assessing the Suitability of Sediment Soil to Be Reused by Different Soil Treatments for Forest Agriculture
Assessing the Suitability of Sediment Soil to Be Reused by Different Soil Treatments for Forest Agriculture
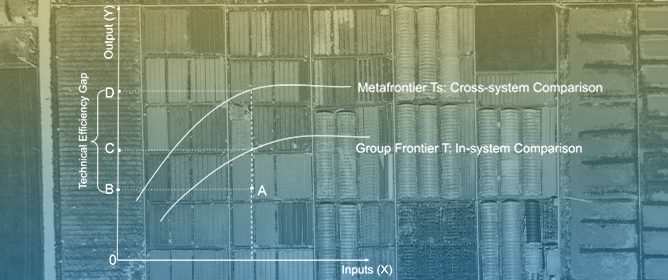 Integrated vs. Specialized Farming Systems for Sustainable Food Production: Comparative Analysis of Systems’ Technical Efficiency in Nebraska
Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, cross-disciplinary, scholarly, peer-reviewed and open access journal of environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings. It provides an advanced forum for studies related to sustainability and sustainable development, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) and International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first
decision is provided to authors approximately 18.3 days after submission; acceptance
to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in
this journal in the first half of 2023).
Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
subject
Imprint Information
get_app
Journal Flyer
Open Access
ISSN: 2071-1050
Latest Articles
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Categorization of Loads in Educational Institutions to Effectively Manage Peak Demand and Minimize Energy Cost Using an Intelligent Load Management Technique
by
Integrated vs. Specialized Farming Systems for Sustainable Food Production: Comparative Analysis of Systems’ Technical Efficiency in Nebraska
Journal Description
Sustainability
Sustainability
is an international, cross-disciplinary, scholarly, peer-reviewed and open access journal of environmental, cultural, economic, and social sustainability of human beings. It provides an advanced forum for studies related to sustainability and sustainable development, and is published semimonthly online by MDPI. The Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) and International Council for Research and Innovation in Building and Construction (CIB) are affiliated with Sustainability and their members receive discounts of the article processing charge.
Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE and SSCI (Web of Science), GEOBASE, GeoRef, Inspec, AGRIS, RePEc, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Environmental Studies) / CiteScore - Q1 (Geography, Planning and Development)
Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first
decision is provided to authors approximately 18.3 days after submission; acceptance
to publication is undertaken in 3.5 days (median values for papers published in
this journal in the first half of 2023).
Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about Sustainability.
Companion journals for Sustainability include: World, Sustainable Chemistry, Conservation, Future Transportation, Architecture, Standards, Merits and Wind.
Impact Factor:
3.9 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.0 (2022)
subject
Imprint Information
get_app
Journal Flyer
Open Access
ISSN: 2071-1050
Latest Articles
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Categorization of Loads in Educational Institutions to Effectively Manage Peak Demand and Minimize Energy Cost Using an Intelligent Load Management Technique
by
 Priyadharshini Ramu, Priyadharshini Ramu,  Sivasankar Gangatharan, Sivasankar Gangatharan,  Sankar Rangasamy and Sankar Rangasamy and  Lucian Mihet-Popa
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12209; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612209 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
The inclusion of photovoltaics (PV) in electric power supply systems continues to be a significant factor in global interest. However, solar power exhibits intermittent uncertainty and is further unpredictable. Accurate solar generation prediction and efficient utilization are mandatory for power distribution management and
[...] Read more.
The inclusion of photovoltaics (PV) in electric power supply systems continues to be a significant factor in global interest. However, solar power exhibits intermittent uncertainty and is further unpredictable. Accurate solar generation prediction and efficient utilization are mandatory for power distribution management and demand-side management. Peak demand management and reducing energy costs can be effectively tackled through the implementation of a reliable solar power forecasting system and its efficient utilization. In this regard, the proposed work is related to efficiently managing solar PV power and optimizing power distribution using an enhanced reinforced binary particle swarm optimization (RBPSO) technique. This DSM (demand-side management) strategy involves utilizing a forecast of solar PV generation for the upcoming day and adjusting the consumption schedule of the load to decrease the highest energy demand. The proposed approach improves user comfort by adjusting the non-interruptible and flexible institutional load through clipping and shifting techniques. To evaluate the effectiveness of this approach, its performance is assessed by analyzing the peak demand range and PAR (peak-to-average ratio). It is then compared to the conventional genetic algorithm to determine its effectiveness. Simulation results obtained using MATLAB show that the PAR peak demand before DSM was found to be 1.8602 kW and 378.06 kW, and after DSM, it was reduced to 0.7211 kW and 266.54 kW. This indicates a 29% reduction in Peak demand and performance compared to the conventional genetic algorithm (GA).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Lucian Mihet-Popa
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12209; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612209 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
The inclusion of photovoltaics (PV) in electric power supply systems continues to be a significant factor in global interest. However, solar power exhibits intermittent uncertainty and is further unpredictable. Accurate solar generation prediction and efficient utilization are mandatory for power distribution management and
[...] Read more.
The inclusion of photovoltaics (PV) in electric power supply systems continues to be a significant factor in global interest. However, solar power exhibits intermittent uncertainty and is further unpredictable. Accurate solar generation prediction and efficient utilization are mandatory for power distribution management and demand-side management. Peak demand management and reducing energy costs can be effectively tackled through the implementation of a reliable solar power forecasting system and its efficient utilization. In this regard, the proposed work is related to efficiently managing solar PV power and optimizing power distribution using an enhanced reinforced binary particle swarm optimization (RBPSO) technique. This DSM (demand-side management) strategy involves utilizing a forecast of solar PV generation for the upcoming day and adjusting the consumption schedule of the load to decrease the highest energy demand. The proposed approach improves user comfort by adjusting the non-interruptible and flexible institutional load through clipping and shifting techniques. To evaluate the effectiveness of this approach, its performance is assessed by analyzing the peak demand range and PAR (peak-to-average ratio). It is then compared to the conventional genetic algorithm to determine its effectiveness. Simulation results obtained using MATLAB show that the PAR peak demand before DSM was found to be 1.8602 kW and 378.06 kW, and after DSM, it was reduced to 0.7211 kW and 266.54 kW. This indicates a 29% reduction in Peak demand and performance compared to the conventional genetic algorithm (GA).
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Urban Waste Management and Prediction through Socio-Economic Values and Visualizing the Spatiotemporal Relationship on an Advanced GIS-Based Dashboard by Shixiong Xu, Shixiong Xu,  Sara Shirowzhan and Sara Shirowzhan and  Samad M. E. Sepasgozar
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12208; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612208 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Enhancing data-driven decision-making is vital for waste authorities. Although few studies have explored the influence of socio-economic indicators on waste tonnage, comprehensive analysis of urban waste data focusing on geographical information is also scarce. There is a dearth of dashboards for visualizing waste
[...] Read more.
Enhancing data-driven decision-making is vital for waste authorities. Although few studies have explored the influence of socio-economic indicators on waste tonnage, comprehensive analysis of urban waste data focusing on geographical information is also scarce. There is a dearth of dashboards for visualizing waste tonnage with spatial relationship maps. This study aims to present a prediction model useful for estimating urban waste by using personal income (I), the number of income earners (E), land values (L), the estimated resident population (P) and population density (D), called the IELPD measures. An innovative approach is developed to identify the correlation between urban household waste data and socio-economic factors and develop an advanced dashboard based on a geographic information system (GIS). To accomplish this, relationship maps and regression analysis are deployed to visualize household waste data spanning six years of waste production in New South Wales, Australia, classified into three categories: recyclable, residual and organic (RRO) wastes. Furthermore, this classification enables accessing the association between these three waste categories and the IELPD metrics. And there are four types of visualization generated, that is, thematic mapping, spatial relationship maps, correlation matrices and dashboard development. The regression analysis shows a substantial association between RRO waste tonnage, population changes and a minor correlation with land values. Overall, this study contributes to urban waste data storytelling and its spatiotemporal associations with socio-economic determinants. This paper offers a valuable prediction model of the IELPD metrics to estimate urban waste and visualize them in a dashboard allowing practitioners and decision-makers to track trends in the RRO waste stream in urban waste generally.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Samad M. E. Sepasgozar
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12208; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612208 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Enhancing data-driven decision-making is vital for waste authorities. Although few studies have explored the influence of socio-economic indicators on waste tonnage, comprehensive analysis of urban waste data focusing on geographical information is also scarce. There is a dearth of dashboards for visualizing waste
[...] Read more.
Enhancing data-driven decision-making is vital for waste authorities. Although few studies have explored the influence of socio-economic indicators on waste tonnage, comprehensive analysis of urban waste data focusing on geographical information is also scarce. There is a dearth of dashboards for visualizing waste tonnage with spatial relationship maps. This study aims to present a prediction model useful for estimating urban waste by using personal income (I), the number of income earners (E), land values (L), the estimated resident population (P) and population density (D), called the IELPD measures. An innovative approach is developed to identify the correlation between urban household waste data and socio-economic factors and develop an advanced dashboard based on a geographic information system (GIS). To accomplish this, relationship maps and regression analysis are deployed to visualize household waste data spanning six years of waste production in New South Wales, Australia, classified into three categories: recyclable, residual and organic (RRO) wastes. Furthermore, this classification enables accessing the association between these three waste categories and the IELPD metrics. And there are four types of visualization generated, that is, thematic mapping, spatial relationship maps, correlation matrices and dashboard development. The regression analysis shows a substantial association between RRO waste tonnage, population changes and a minor correlation with land values. Overall, this study contributes to urban waste data storytelling and its spatiotemporal associations with socio-economic determinants. This paper offers a valuable prediction model of the IELPD metrics to estimate urban waste and visualize them in a dashboard allowing practitioners and decision-makers to track trends in the RRO waste stream in urban waste generally.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle The Effect of Esports Content Attributes on Viewing Flow and Well-Being: A Focus on the Moderating Effect of Esports Involvement by Chaoyu Yin, Chaoyu Yin,  Yihan Huang, Yihan Huang,  Daehwan Kim and Daehwan Kim and  Kyungun Kim
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12207; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612207 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Despite being recognized as a global entertainment phenomenon, the nature of esports has been a subject of ongoing debate due to its content attributes and the controversial impact it has on individuals’ physical and mental well-being. We contend that the fundamental source of
[...] Read more.
Despite being recognized as a global entertainment phenomenon, the nature of esports has been a subject of ongoing debate due to its content attributes and the controversial impact it has on individuals’ physical and mental well-being. We contend that the fundamental source of contention lies within the inherent content attributes of esports. Drawing on uses and gratification theory (UG) and cognitive appraisal theory, the purpose of the current study was to explore how esports content attributes and viewers’ individual characteristics (esports involvement) influence the viewer’s experience (flow experience) and well-being (happiness and vitality). The results of a latent moderated structural equations (LMS) modeling analysis using a total of 539 viewers revealed that entertainment, reliability, and diversity significantly influenced flow experience, which in turn influenced viewers’ happiness and vitality. Esports involvement was found to have moderating effects on the relationship between reliability and usefulness attributes and flow experience. The findings of this research provide important contributions to the literature and have implications for sport marketing managers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainability of Sport Management in the Post-COVID19 Era)
►▼
Show Figures Kyungun Kim
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12207; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612207 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Despite being recognized as a global entertainment phenomenon, the nature of esports has been a subject of ongoing debate due to its content attributes and the controversial impact it has on individuals’ physical and mental well-being. We contend that the fundamental source of
[...] Read more.
Despite being recognized as a global entertainment phenomenon, the nature of esports has been a subject of ongoing debate due to its content attributes and the controversial impact it has on individuals’ physical and mental well-being. We contend that the fundamental source of contention lies within the inherent content attributes of esports. Drawing on uses and gratification theory (UG) and cognitive appraisal theory, the purpose of the current study was to explore how esports content attributes and viewers’ individual characteristics (esports involvement) influence the viewer’s experience (flow experience) and well-being (happiness and vitality). The results of a latent moderated structural equations (LMS) modeling analysis using a total of 539 viewers revealed that entertainment, reliability, and diversity significantly influenced flow experience, which in turn influenced viewers’ happiness and vitality. Esports involvement was found to have moderating effects on the relationship between reliability and usefulness attributes and flow experience. The findings of this research provide important contributions to the literature and have implications for sport marketing managers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainability of Sport Management in the Post-COVID19 Era)
►▼
Show Figures
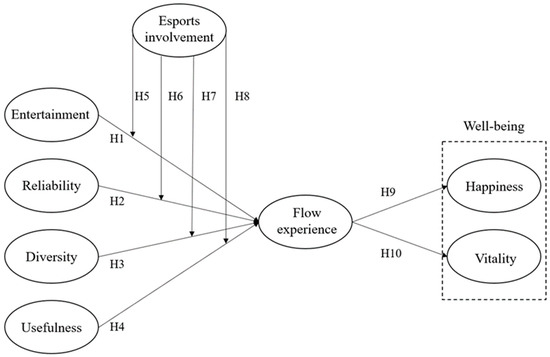 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Promoting Sustainable Food Practices in Food Service Industry: An Empirical Investigation on Saudi Arabian Restaurants by Ahmed Hassan Abdou, Ahmed Hassan Abdou,  Thowayeb H. Hassan and Thowayeb H. Hassan and  Amany E. Salem
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12206; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612206 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
While facing environmental challenges and rising concerns around food security and equitable access to nutritious food, sustainable food practices (SFPs) have emerged as a crucial focus area for the restaurant industry. Hence, this study aims to investigate key drivers of promoting SFPs, including
[...] Read more.
While facing environmental challenges and rising concerns around food security and equitable access to nutritious food, sustainable food practices (SFPs) have emerged as a crucial focus area for the restaurant industry. Hence, this study aims to investigate key drivers of promoting SFPs, including customers’ and stakeholders’ sustainable behaviors, governmental laws and regulations around sustainability, the commitment of restaurants to combat climate change, the financial and non-financial outcomes of adopting SFPs, and restaurants’ values and culture toward sustainability. In addition, it explores the power of promoting these practices in driving restaurants’ economic, environmental, and social performance. To achieve these objectives, an online survey was administered to restaurant owners and top managers interested in implementing these practices. Accordingly, eight hypotheses, which explored the direct relationships between this study’s variables, were tested using PLS-SEM with bootstrapping. Based on 221 valid responses, this study revealed that all proposed paths were significant and aligned with each hypothesis. Notably, sustainable behavior exhibited by customers and stakeholders had the greatest influence on promoting SFPs, followed by the values and culture of restaurants related to sustainability and restaurants’ commitment to combatting climate change. Additionally, promoting SFPs was a crucial predictor for enhancing restaurants’ economic, environmental, and social performance, respectively. Upon these findings, restaurant owners and top managers should build a solid framework for promoting SFPs in their establishments by focusing on these factors, thereby improving their overall economic, environmental, and social performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental, Economic, and Social Sustainability in Food Services)
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Cities, Smart Investments: A Characterization of “A Thousand Days-San Miguel”, a Program for Vulnerable Early Childhood in Argentina
by Amany E. Salem
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12206; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612206 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
While facing environmental challenges and rising concerns around food security and equitable access to nutritious food, sustainable food practices (SFPs) have emerged as a crucial focus area for the restaurant industry. Hence, this study aims to investigate key drivers of promoting SFPs, including
[...] Read more.
While facing environmental challenges and rising concerns around food security and equitable access to nutritious food, sustainable food practices (SFPs) have emerged as a crucial focus area for the restaurant industry. Hence, this study aims to investigate key drivers of promoting SFPs, including customers’ and stakeholders’ sustainable behaviors, governmental laws and regulations around sustainability, the commitment of restaurants to combat climate change, the financial and non-financial outcomes of adopting SFPs, and restaurants’ values and culture toward sustainability. In addition, it explores the power of promoting these practices in driving restaurants’ economic, environmental, and social performance. To achieve these objectives, an online survey was administered to restaurant owners and top managers interested in implementing these practices. Accordingly, eight hypotheses, which explored the direct relationships between this study’s variables, were tested using PLS-SEM with bootstrapping. Based on 221 valid responses, this study revealed that all proposed paths were significant and aligned with each hypothesis. Notably, sustainable behavior exhibited by customers and stakeholders had the greatest influence on promoting SFPs, followed by the values and culture of restaurants related to sustainability and restaurants’ commitment to combatting climate change. Additionally, promoting SFPs was a crucial predictor for enhancing restaurants’ economic, environmental, and social performance, respectively. Upon these findings, restaurant owners and top managers should build a solid framework for promoting SFPs in their establishments by focusing on these factors, thereby improving their overall economic, environmental, and social performance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Environmental, Economic, and Social Sustainability in Food Services)
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Sustainable Cities, Smart Investments: A Characterization of “A Thousand Days-San Miguel”, a Program for Vulnerable Early Childhood in Argentina
by
 Maria Sol Gonzalez and Maria Sol Gonzalez and  Maria Emma Santos
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12205; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612205 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, we provide a thorough description of the “Programa de Acompañamiento Familiar Mil Días” (A Thousand Days, Mil Días), introduced in 2015 in the Municipality of San Miguel, Buenos Aires, Argentina. The program is targeted at pregnant women and mothers with
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we provide a thorough description of the “Programa de Acompañamiento Familiar Mil Días” (A Thousand Days, Mil Días), introduced in 2015 in the Municipality of San Miguel, Buenos Aires, Argentina. The program is targeted at pregnant women and mothers with children of up to two years of age who are in a situation of extreme social and health vulnerability. While the target relevant period is the first thousand days of life, from gestation to two years of age, the intended duration is about a year, or until entrance criteria are overcome. We combine statistical analysis of the program’s primary data with qualitative analysis from two in-depth interviews. Our evidence confirms that Mil Días-SM effectively reaches a highly vulnerable population that exhibits interlocking material and educational deprivations, frequently combined with conflict-home environments, and children experiencing health neglect. The one-on-one mentoring provided through the program, along with a battery of other interventions, brings knowledge and support to these families. Children start receiving appropriate stimuli, mothers become aware of the importance of health care for them and their children, and they start feeling more empowered to take command of their lives and families. While the program exhibits remarkable attributes, we identify three aspects in which it could be improved: extending the intended duration time, reducing its dropout rate devising tools to retain the most vulnerable cases, and scaling up its coverage. Current evidence suggests programs like Mil Días are smart investments that can simultaneously contribute to achieving several Sustainable Development Goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Cities: Challenges and Potential Solutions)
►▼
Show Figures Maria Emma Santos
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12205; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612205 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In this paper, we provide a thorough description of the “Programa de Acompañamiento Familiar Mil Días” (A Thousand Days, Mil Días), introduced in 2015 in the Municipality of San Miguel, Buenos Aires, Argentina. The program is targeted at pregnant women and mothers with
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we provide a thorough description of the “Programa de Acompañamiento Familiar Mil Días” (A Thousand Days, Mil Días), introduced in 2015 in the Municipality of San Miguel, Buenos Aires, Argentina. The program is targeted at pregnant women and mothers with children of up to two years of age who are in a situation of extreme social and health vulnerability. While the target relevant period is the first thousand days of life, from gestation to two years of age, the intended duration is about a year, or until entrance criteria are overcome. We combine statistical analysis of the program’s primary data with qualitative analysis from two in-depth interviews. Our evidence confirms that Mil Días-SM effectively reaches a highly vulnerable population that exhibits interlocking material and educational deprivations, frequently combined with conflict-home environments, and children experiencing health neglect. The one-on-one mentoring provided through the program, along with a battery of other interventions, brings knowledge and support to these families. Children start receiving appropriate stimuli, mothers become aware of the importance of health care for them and their children, and they start feeling more empowered to take command of their lives and families. While the program exhibits remarkable attributes, we identify three aspects in which it could be improved: extending the intended duration time, reducing its dropout rate devising tools to retain the most vulnerable cases, and scaling up its coverage. Current evidence suggests programs like Mil Días are smart investments that can simultaneously contribute to achieving several Sustainable Development Goals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Cities: Challenges and Potential Solutions)
►▼
Show Figures
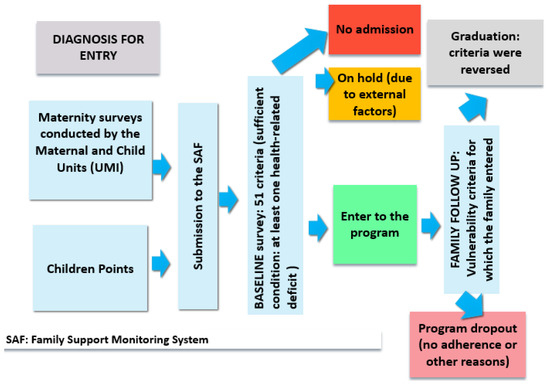 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessReview Energy Management Systems for Smart Electric Railway Networks: A Methodological Review by Mohsen Davoodi, Mohsen Davoodi,  Hamed Jafari Kaleybar, Hamed Jafari Kaleybar,  Morris Brenna and Morris Brenna and  Dario Zaninelli
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12204; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612204 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Energy shortage is one of the major concerns in today’s world. As a consumer of electrical energy, the electric railway system (ERS), due to trains, stations, and commercial users, intakes an enormous amount of electricity. Increasing greenhouse gases (GHG) and CO2 emissions,
[...] Read more.
Energy shortage is one of the major concerns in today’s world. As a consumer of electrical energy, the electric railway system (ERS), due to trains, stations, and commercial users, intakes an enormous amount of electricity. Increasing greenhouse gases (GHG) and CO2 emissions, in addition, have drawn the regard of world leaders as among the most dangerous threats at present; based on research in this field, the transportation sector contributes significantly to this pollution. Railway Energy Management Systems (REMS) are a modern green solution that not only tackle these problems but also, by implementing REMS, electricity can be sold to the grid market. Researchers have been trying to reduce the daily operational costs of smart railway stations, mitigating power quality issues, considering the traction uncertainties and stochastic behavior of Renewable Energy Resources (RERs) and Energy Storage Systems (ESSs), which has a significant impact on total operational cost. In this context, the first main objective of this article is to take a comprehensive review of the literature on REMS and examine closely all the works that have been carried out in this area, and also the REMS architecture and configurations are clarified as well. The secondary objective of this article is to analyze both traditional and modern methods utilized in REMS and conduct a thorough comparison of them. In order to provide a comprehensive analysis in this field, over 120 publications have been compiled, listed, and categorized. The study highlights the potential of leveraging RERs for cost reduction and sustainability. Evaluating factors including speed, simplicity, efficiency, accuracy, and ability to handle stochastic behavior and constraints, the strengths and limitations of each optimization method are elucidated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Energy Technology and Sustainable Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures Dario Zaninelli
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12204; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612204 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Energy shortage is one of the major concerns in today’s world. As a consumer of electrical energy, the electric railway system (ERS), due to trains, stations, and commercial users, intakes an enormous amount of electricity. Increasing greenhouse gases (GHG) and CO2 emissions,
[...] Read more.
Energy shortage is one of the major concerns in today’s world. As a consumer of electrical energy, the electric railway system (ERS), due to trains, stations, and commercial users, intakes an enormous amount of electricity. Increasing greenhouse gases (GHG) and CO2 emissions, in addition, have drawn the regard of world leaders as among the most dangerous threats at present; based on research in this field, the transportation sector contributes significantly to this pollution. Railway Energy Management Systems (REMS) are a modern green solution that not only tackle these problems but also, by implementing REMS, electricity can be sold to the grid market. Researchers have been trying to reduce the daily operational costs of smart railway stations, mitigating power quality issues, considering the traction uncertainties and stochastic behavior of Renewable Energy Resources (RERs) and Energy Storage Systems (ESSs), which has a significant impact on total operational cost. In this context, the first main objective of this article is to take a comprehensive review of the literature on REMS and examine closely all the works that have been carried out in this area, and also the REMS architecture and configurations are clarified as well. The secondary objective of this article is to analyze both traditional and modern methods utilized in REMS and conduct a thorough comparison of them. In order to provide a comprehensive analysis in this field, over 120 publications have been compiled, listed, and categorized. The study highlights the potential of leveraging RERs for cost reduction and sustainability. Evaluating factors including speed, simplicity, efficiency, accuracy, and ability to handle stochastic behavior and constraints, the strengths and limitations of each optimization method are elucidated.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Energy Technology and Sustainable Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures
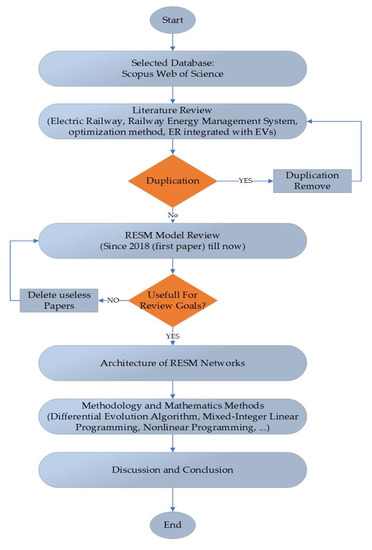 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Odour Perception Using a Sniffing Team at a Municipal Solid Waste Treatment Plant: A Case Study by Izabela Konkol, Izabela Konkol,  Robert Tylingo, Robert Tylingo,  Szymon Mania and Szymon Mania and  Adam Cenian
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12203; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612203 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
The monitoring of odour intensity, generated by a landfill area, is a difficult activity since it is a multi-source problem with discontinuous odour emissions. A modified sniffing team method is described here and applied to determine the main odour sources in a landfill
[...] Read more.
The monitoring of odour intensity, generated by a landfill area, is a difficult activity since it is a multi-source problem with discontinuous odour emissions. A modified sniffing team method is described here and applied to determine the main odour sources in a landfill located in Pomerania, Poland. Four consecutive test sessions were performed during the following months: August, December, April, and June. It was found that the main odour sources are as follows: a closed-chamber composting facility for leach storage; the site wherein technological operations associated with compost turn-over during open-air aeration processes are performed; and the landfill site. The results of the sniffing team method present the indicative values of sensory testing. The application of the presented method was limited by disturbances due to changing atmospheric conditions. The calculated odour intensities and concentrations correspond with real sensitive perceptions of the tested environment.
Full article
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Dust in Open Pit Coal Mine Crushing Stations and Closed Dust Reduction Methods
by Adam Cenian
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12203; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612203 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
The monitoring of odour intensity, generated by a landfill area, is a difficult activity since it is a multi-source problem with discontinuous odour emissions. A modified sniffing team method is described here and applied to determine the main odour sources in a landfill
[...] Read more.
The monitoring of odour intensity, generated by a landfill area, is a difficult activity since it is a multi-source problem with discontinuous odour emissions. A modified sniffing team method is described here and applied to determine the main odour sources in a landfill located in Pomerania, Poland. Four consecutive test sessions were performed during the following months: August, December, April, and June. It was found that the main odour sources are as follows: a closed-chamber composting facility for leach storage; the site wherein technological operations associated with compost turn-over during open-air aeration processes are performed; and the landfill site. The results of the sniffing team method present the indicative values of sensory testing. The application of the presented method was limited by disturbances due to changing atmospheric conditions. The calculated odour intensities and concentrations correspond with real sensitive perceptions of the tested environment.
Full article
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Research on the Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Dust in Open Pit Coal Mine Crushing Stations and Closed Dust Reduction Methods
by
 Zhichao Liu, Zhichao Liu,  Zhongchen Ao, Zhongchen Ao,  Wei Zhou, Wei Zhou,  Baowei Zhang, Baowei Zhang,  Jingfu Niu, Jingfu Niu,  Zhiming Wang, Zhiming Wang,  Lijie Liu, Lijie Liu,  Zexuan Yang, Zexuan Yang,  Kun Xu, Kun Xu,  Wenqi Lu and Wenqi Lu and  Lixia Zhu
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12202; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612202 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
As an important link in open-pit mining production, the crushing station produces a large amount of dust during the production process. Dust has the characteristics of a wide spread area, great harm, and difficult governance. Therefore, dust control has become a key issue
[...] Read more.
As an important link in open-pit mining production, the crushing station produces a large amount of dust during the production process. Dust has the characteristics of a wide spread area, great harm, and difficult governance. Therefore, dust control has become a key issue that needs to be solved in open-pit mining. In this article, we assess results after high-speed cameras and dust concentration detectors are installed around the crushing station to monitor the dust concentration in the surrounding air. It is found that in the air, dust with a particle size of less than 2.5 μm accounts for 67.43%, less than 10 μm accounts for 17.30%, and less than 100 μm accounts for 15.27%. In settled dust on the ground, particles with a particle size of less than 100 μm account for 42.69% of the sample, and particles less than 10 μm account for 16.60% of the sample. Secondly, physical and chemical properties testing is conducted on the dust. XRD test results show that SiO2 in the dust accounts for 65.80%; XRF test results show that the oxide Al2O3 in the dust accounts for up to 46.84%; ICP test results show that the element Al accounts for 42.62% of the total amount of trace elements detected; and Si accounts for 35.11%, clarifying the content of harmful substances to the human body. Finally, Fluent software, Ansys 2020 R1, is used to simulate the diffusion law of dust under different states of the crushing station, including an open state, a closed state, and the installation of a dust removal system. Based on the simulation results and the actual situation on site, the optimal dust reduction method suitable for the crushing station is proposed, and the diffusion law of dust under this method is simulated. The tracked dust shows that the dust removal efficiency of PM2.5 reaches 97.00%, PM10 reaches 99.60%, and TSP reaches 98.30%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Intelligent and Sustainable Mining)
►▼
Show Figures Lixia Zhu
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12202; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612202 (registering DOI) - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
As an important link in open-pit mining production, the crushing station produces a large amount of dust during the production process. Dust has the characteristics of a wide spread area, great harm, and difficult governance. Therefore, dust control has become a key issue
[...] Read more.
As an important link in open-pit mining production, the crushing station produces a large amount of dust during the production process. Dust has the characteristics of a wide spread area, great harm, and difficult governance. Therefore, dust control has become a key issue that needs to be solved in open-pit mining. In this article, we assess results after high-speed cameras and dust concentration detectors are installed around the crushing station to monitor the dust concentration in the surrounding air. It is found that in the air, dust with a particle size of less than 2.5 μm accounts for 67.43%, less than 10 μm accounts for 17.30%, and less than 100 μm accounts for 15.27%. In settled dust on the ground, particles with a particle size of less than 100 μm account for 42.69% of the sample, and particles less than 10 μm account for 16.60% of the sample. Secondly, physical and chemical properties testing is conducted on the dust. XRD test results show that SiO2 in the dust accounts for 65.80%; XRF test results show that the oxide Al2O3 in the dust accounts for up to 46.84%; ICP test results show that the element Al accounts for 42.62% of the total amount of trace elements detected; and Si accounts for 35.11%, clarifying the content of harmful substances to the human body. Finally, Fluent software, Ansys 2020 R1, is used to simulate the diffusion law of dust under different states of the crushing station, including an open state, a closed state, and the installation of a dust removal system. Based on the simulation results and the actual situation on site, the optimal dust reduction method suitable for the crushing station is proposed, and the diffusion law of dust under this method is simulated. The tracked dust shows that the dust removal efficiency of PM2.5 reaches 97.00%, PM10 reaches 99.60%, and TSP reaches 98.30%.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Intelligent and Sustainable Mining)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Mapping of Evapotranspiration and Determination of the Water Footprint of a Potato Crop Grown in Hyper-Arid Regions in Saudi Arabia by Rangaswamy Madugundu, Rangaswamy Madugundu,  Khalid A. Al-Gaadi, Khalid A. Al-Gaadi,  ElKamil Tola, ElKamil Tola,  Salah El-Hendawy and Salah El-Hendawy and  Samy A. Marey
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12201; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612201 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Seasonal quantification of a crop’s evapotranspiration (ET) and water footprint (WF) is essential for sustainable agriculture. Therefore, this study was conducted to estimate the ET and WF of an irrigated potato crop using satellite imagery of Landsat and Sentinel-2 sensors. The Simplified Surface
[...] Read more.
Seasonal quantification of a crop’s evapotranspiration (ET) and water footprint (WF) is essential for sustainable agriculture. Therefore, this study was conducted to estimate the ET and WF of an irrigated potato crop using satellite imagery of Landsat and Sentinel-2 sensors. The Simplified Surface Energy Balance (SSEB) algorithm was used to evaluate the crop water use (ETa) for potato fields belonging to the Saudi Agricultural Development Company, located in the Wadi-Ad-Dawasir region, Saudi Arabia. Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI), and land surface temperature (LSD) were computed for Landsat and Sentinel-2 datasets, which were used as inputs for mapping the potato tuber yield and, subsequently, the WF. The results indicated that the NDVI showed the best accuracy for the prediction of the potato tuber yield (R2 = 0.72, P > F = 0.021) followed by the SAVI (R2 = 0.64, P > F = 0.018), compared to the field harvested actual yield (YA). A comparison between the satellite-based ETa and the actual amount of water applied (WA) for irrigation showed a good correlation (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 4.4%, MBE = 12.9%). The WF of the potatoes in the study area was estimated at values between 475 and 357 m3 t−1 for the early (September–December) and late (December–April) growing periods, respectively. A major portion (99.2%) of the WF was accounted for from irrigation with variations of 18.5% and 3.5% for early- and late-planted potatoes, respectively, compared to the baseline (crop planted in season). In conclusion, the results showed the possibility of satisfactorily estimating the WF using the SSEB algorithm by integrating the Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 datasets. In general, the high rates of ET in the early planting season led to higher WF values compared to the in-season and late planting dates; this will help in selecting suitable planting dates for potato crops in the study area and areas with similar environments, which enhances the opportunities for sustainable management of irrigation water.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Management of Water Resources in Arid Environments – Innovative Approaches)
►▼
Show Figures Samy A. Marey
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12201; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612201 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Seasonal quantification of a crop’s evapotranspiration (ET) and water footprint (WF) is essential for sustainable agriculture. Therefore, this study was conducted to estimate the ET and WF of an irrigated potato crop using satellite imagery of Landsat and Sentinel-2 sensors. The Simplified Surface
[...] Read more.
Seasonal quantification of a crop’s evapotranspiration (ET) and water footprint (WF) is essential for sustainable agriculture. Therefore, this study was conducted to estimate the ET and WF of an irrigated potato crop using satellite imagery of Landsat and Sentinel-2 sensors. The Simplified Surface Energy Balance (SSEB) algorithm was used to evaluate the crop water use (ETa) for potato fields belonging to the Saudi Agricultural Development Company, located in the Wadi-Ad-Dawasir region, Saudi Arabia. Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI), and land surface temperature (LSD) were computed for Landsat and Sentinel-2 datasets, which were used as inputs for mapping the potato tuber yield and, subsequently, the WF. The results indicated that the NDVI showed the best accuracy for the prediction of the potato tuber yield (R2 = 0.72, P > F = 0.021) followed by the SAVI (R2 = 0.64, P > F = 0.018), compared to the field harvested actual yield (YA). A comparison between the satellite-based ETa and the actual amount of water applied (WA) for irrigation showed a good correlation (R2 = 0.89, RMSE = 4.4%, MBE = 12.9%). The WF of the potatoes in the study area was estimated at values between 475 and 357 m3 t−1 for the early (September–December) and late (December–April) growing periods, respectively. A major portion (99.2%) of the WF was accounted for from irrigation with variations of 18.5% and 3.5% for early- and late-planted potatoes, respectively, compared to the baseline (crop planted in season). In conclusion, the results showed the possibility of satisfactorily estimating the WF using the SSEB algorithm by integrating the Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 datasets. In general, the high rates of ET in the early planting season led to higher WF values compared to the in-season and late planting dates; this will help in selecting suitable planting dates for potato crops in the study area and areas with similar environments, which enhances the opportunities for sustainable management of irrigation water.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Management of Water Resources in Arid Environments – Innovative Approaches)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Spatial and Temporal Evolutionary Characteristics of Vegetation in Different Geomorphic Zones of Loess Plateau and Its Driving Factor Analysis by Xue Li, Xue Li,  Kunxia Yu, Kunxia Yu,  Xiang Zhang, Xiang Zhang,  Guojun Zhang, Guojun Zhang,  Zhanbin Li, Zhanbin Li,  Peng Li, Peng Li,  Xiaoming Zhang, Xiaoming Zhang,  Yang Zhao and Yang Zhao and  Wentao Ma
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12200; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612200 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Based on MODIS NDVI and a meteorological dataset, this study analyzed the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation cover in different geomorphic zones of Loess Plateau (LP) from 2000 to 2020 with trend analysis, partial correlation, residual analysis and the CA–Markov method
[...] Read more.
Based on MODIS NDVI and a meteorological dataset, this study analyzed the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation cover in different geomorphic zones of Loess Plateau (LP) from 2000 to 2020 with trend analysis, partial correlation, residual analysis and the CA–Markov method and discussed the driving factors. The research results show that: (1) There are spatial differences in vegetation coverage in different geomorphic regions. The Loess Hills and Forests zone (LF) exhibits the highest coverage, with a multi-year average of 86.64%, and the Arid Grassland (AG) has the poorest vegetation with only 8.53%. Overall, there has been significant improvement in vegetation coverage over the past two decades, although certain geomorphic zones, particularly the Highland Steppe zone (HS) and Alluvial Plains zone (AP), show signs of degradation. (2) Relative humidity has the greatest impact on vegetation among the three climate factors, i.e., relative humidity, precipitation and temperature. Relative humidity predominantly promotes vegetation in all geomorphic zones. Temperature generally inhibits vegetation growth, except in the Wind Sandy zone (WA) and AG. The impact of precipitation on vegetation depends on the region. A lag effect is observed, with temperature and humidity showing a one-month lag and precipitation showing a two-month lag on vegetation response. (3) Human activities play a crucial role in promoting vegetation, particularly in the WA zone, in which the percentage of area where human activities contribute to vegetation has changed from 13.80% to 86.85%, an increase of 73.05%, while the HS experiences an inhibitory effect due to overgrazing and water resource overutilization. Similarly, the AP zone’s vegetation growth is hindered by urban development and land use changes. (4) Land use change significantly impacts vegetation dynamics on the LP. Over the past two decades, the area of forest lawn increased by 122,800 km2, which is 1.5 times more than the area of reduction. However, conversion to building land has hindered vegetation growth in certain regions. A comprehensive strategy is required to conserve land resources and promote healthy vegetation growth on the LP.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Erosion and Water and Soil Conservation)
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Green and Environmental Marketing Strategies and Ethical Consumption: Evidence from the Tourism Sector
by Wentao Ma
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12200; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612200 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Based on MODIS NDVI and a meteorological dataset, this study analyzed the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation cover in different geomorphic zones of Loess Plateau (LP) from 2000 to 2020 with trend analysis, partial correlation, residual analysis and the CA–Markov method
[...] Read more.
Based on MODIS NDVI and a meteorological dataset, this study analyzed the spatial and temporal variation characteristics of vegetation cover in different geomorphic zones of Loess Plateau (LP) from 2000 to 2020 with trend analysis, partial correlation, residual analysis and the CA–Markov method and discussed the driving factors. The research results show that: (1) There are spatial differences in vegetation coverage in different geomorphic regions. The Loess Hills and Forests zone (LF) exhibits the highest coverage, with a multi-year average of 86.64%, and the Arid Grassland (AG) has the poorest vegetation with only 8.53%. Overall, there has been significant improvement in vegetation coverage over the past two decades, although certain geomorphic zones, particularly the Highland Steppe zone (HS) and Alluvial Plains zone (AP), show signs of degradation. (2) Relative humidity has the greatest impact on vegetation among the three climate factors, i.e., relative humidity, precipitation and temperature. Relative humidity predominantly promotes vegetation in all geomorphic zones. Temperature generally inhibits vegetation growth, except in the Wind Sandy zone (WA) and AG. The impact of precipitation on vegetation depends on the region. A lag effect is observed, with temperature and humidity showing a one-month lag and precipitation showing a two-month lag on vegetation response. (3) Human activities play a crucial role in promoting vegetation, particularly in the WA zone, in which the percentage of area where human activities contribute to vegetation has changed from 13.80% to 86.85%, an increase of 73.05%, while the HS experiences an inhibitory effect due to overgrazing and water resource overutilization. Similarly, the AP zone’s vegetation growth is hindered by urban development and land use changes. (4) Land use change significantly impacts vegetation dynamics on the LP. Over the past two decades, the area of forest lawn increased by 122,800 km2, which is 1.5 times more than the area of reduction. However, conversion to building land has hindered vegetation growth in certain regions. A comprehensive strategy is required to conserve land resources and promote healthy vegetation growth on the LP.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Soil Erosion and Water and Soil Conservation)
get_app
Open AccessArticle
Green and Environmental Marketing Strategies and Ethical Consumption: Evidence from the Tourism Sector
by
 Abdelmohsen A. Nassani, Abdelmohsen A. Nassani,  Zahid Yousaf, Zahid Yousaf,  Adriana Grigorescu and Adriana Grigorescu and  Alexandra Popa
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12199; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612199 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Sustainable business in the hospitality sector should be designed and restructured to offer services meant to satisfy the customers aware of the ethical behavior toward environment. Green environmental marketing strategies (GES) are based on the desire of the customers to access hospitality services
[...] Read more.
Sustainable business in the hospitality sector should be designed and restructured to offer services meant to satisfy the customers aware of the ethical behavior toward environment. Green environmental marketing strategies (GES) are based on the desire of the customers to access hospitality services with zero or a less negative impact with the adaptation of greening activities. Therefore, this research aims to explore the direct effects of green environmental strategies on ethical consumption and the indirect influence of green marketing and its mediating effect between green environmental strategies and ethical consumption links. Additionally, this research also reveals that psychological aspects play the moderating role in the relationship between GES and ethical consumption. The data were collected from a sample of 545 respondents with the support of Saudi tourism companies, and a structural equation model was used to process them. The findings confirm the positive relationship between green environmental strategy and ethical consumption. The outcomes also corroborate that green marketing is interplaying between green environmental strategy and ethical consumption. In addition, this study validates that psychological aspects strengthen the link between GES and ethical consumption. This study adds to the knowledge in the literature through emphasizing the crucial role of psychological factors in improving green environmental strategies and developing ethical consumption habits among members to increase ethical consumption among tourism companies. The findings support companies from the hospitality sector implementing green sustainable services, to stimulate ethical consumption and to use their competitive advantage in green marketing strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Economy, Resource Efficiency and Sustainable Development)
►▼
Show Figures Alexandra Popa
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12199; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612199 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Sustainable business in the hospitality sector should be designed and restructured to offer services meant to satisfy the customers aware of the ethical behavior toward environment. Green environmental marketing strategies (GES) are based on the desire of the customers to access hospitality services
[...] Read more.
Sustainable business in the hospitality sector should be designed and restructured to offer services meant to satisfy the customers aware of the ethical behavior toward environment. Green environmental marketing strategies (GES) are based on the desire of the customers to access hospitality services with zero or a less negative impact with the adaptation of greening activities. Therefore, this research aims to explore the direct effects of green environmental strategies on ethical consumption and the indirect influence of green marketing and its mediating effect between green environmental strategies and ethical consumption links. Additionally, this research also reveals that psychological aspects play the moderating role in the relationship between GES and ethical consumption. The data were collected from a sample of 545 respondents with the support of Saudi tourism companies, and a structural equation model was used to process them. The findings confirm the positive relationship between green environmental strategy and ethical consumption. The outcomes also corroborate that green marketing is interplaying between green environmental strategy and ethical consumption. In addition, this study validates that psychological aspects strengthen the link between GES and ethical consumption. This study adds to the knowledge in the literature through emphasizing the crucial role of psychological factors in improving green environmental strategies and developing ethical consumption habits among members to increase ethical consumption among tourism companies. The findings support companies from the hospitality sector implementing green sustainable services, to stimulate ethical consumption and to use their competitive advantage in green marketing strategies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Green Economy, Resource Efficiency and Sustainable Development)
►▼
Show Figures
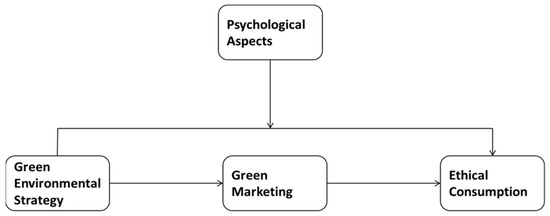 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle The Effect of Green Spaces on User Satisfaction in Historical Cities of Nicosia by Selda İnançoğlu, Selda İnançoğlu,  Havva Arslangazi Uzunahmet and Havva Arslangazi Uzunahmet and  Özge Özden
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12198; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612198 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Urban green spaces (UGS) are one of the most important issues regarding the sustainability of a city. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of UGS on the historical urban texture by measuring user satisfaction. The city of Nicosia was chosen
[...] Read more.
Urban green spaces (UGS) are one of the most important issues regarding the sustainability of a city. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of UGS on the historical urban texture by measuring user satisfaction. The city of Nicosia was chosen as a case study due to its rich texture. This texture has remained in the center of the modern city over time. In line with the purpose of this study, firstly, the existence of UGS, as well as their functionality and contribution to the texture of Nicosia (Walled City), were determined by literature review, field work, and appropriate computer programs. Then, a survey method based on functional factors was applied in order to measure the satisfaction of the users with UGS, and the results were statistically evaluated and compared with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) 26.0 software and the Pearson’s chi-squared test. As a result of the survey, it has been revealed that the existing green areas are insufficient for the people living in the old city of Nicosia. This research has shown that quality green areas that can be used for social activity or relaxation are not available in the old city of Nicosia. In addition, it has been determined that the existing green areas are not clean and safe, there are not enough shading plants, and the existing plants are very neglected. In this context, it is essential to make proper plans for future urban developments in order to have green areas of sufficient scale in the urban fabric.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urbanization and Environmental Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures Özge Özden
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12198; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612198 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Urban green spaces (UGS) are one of the most important issues regarding the sustainability of a city. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of UGS on the historical urban texture by measuring user satisfaction. The city of Nicosia was chosen
[...] Read more.
Urban green spaces (UGS) are one of the most important issues regarding the sustainability of a city. In this study, we aimed to determine the effect of UGS on the historical urban texture by measuring user satisfaction. The city of Nicosia was chosen as a case study due to its rich texture. This texture has remained in the center of the modern city over time. In line with the purpose of this study, firstly, the existence of UGS, as well as their functionality and contribution to the texture of Nicosia (Walled City), were determined by literature review, field work, and appropriate computer programs. Then, a survey method based on functional factors was applied in order to measure the satisfaction of the users with UGS, and the results were statistically evaluated and compared with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) 26.0 software and the Pearson’s chi-squared test. As a result of the survey, it has been revealed that the existing green areas are insufficient for the people living in the old city of Nicosia. This research has shown that quality green areas that can be used for social activity or relaxation are not available in the old city of Nicosia. In addition, it has been determined that the existing green areas are not clean and safe, there are not enough shading plants, and the existing plants are very neglected. In this context, it is essential to make proper plans for future urban developments in order to have green areas of sufficient scale in the urban fabric.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Urbanization and Environmental Sustainability)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Towards a More Sustainable and Less Invasive Approach for the Investigation of Modern and Contemporary Paintings by Teodora Raicu, Teodora Raicu,  Fabiana Zollo, Fabiana Zollo,  Laura Falchi, Laura Falchi,  Elisabetta Barisoni, Elisabetta Barisoni,  Matteo Piccolo and Matteo Piccolo and  Francesca Caterina Izzo
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12197; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612197 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In Heritage Science, sampling is frequently performed for the subsequent diagnostics of modern and contemporary paintings using invasive analytical techniques. However, it endangers the integrity of artworks, and thus, it should be carefully planned and carried out only as a last resort by
[...] Read more.
In Heritage Science, sampling is frequently performed for the subsequent diagnostics of modern and contemporary paintings using invasive analytical techniques. However, it endangers the integrity of artworks, and thus, it should be carefully planned and carried out only as a last resort by specialists. Pigment mixtures have commonly been employed by modern and contemporary artists due to the ease of combining paints on the color palette. Hence, a painting might include both primary/secondary paints and mixtures of those. Therefore, obtaining a sample from a mixture might be sufficient for the identification of the individual primary-colored paints. This study focused on the creation of a user-friendly computational workflow for the analysis of images of paintings for the identification of mixtures using cluster analysis (K-means and Fuzzy C-means clustering). Sixteen modern and contemporary paintings that belong to the International Gallery of Modern Art Ca’ Pesaro in Venice have been selected: seven of them by Guido Cadorin (1892–1976), six by Andreina Rosa (1924–2019), and three by Boris Brollo (b. 1944), and the artworks of the latter being examined for the first time in this study (using Raman and ER–FTIR spectroscopies). It was found that mixtures can be identified in unvarnished paintings that consist of both non-overlapping and vibrant-colored paint layers, like those of Boris Brollo, and overlapping paint layers, like those of Andreina Rosa. Moreover, K-means clustering performs better in the case of non-overlapping colors, whereas Fuzzy C-means in the case of overlapping colors. In contrast, paintings that have been rendered with dark colors and that present a varnish layer, like those of Guido Cadorin, cannot be preliminary investigated in the proposed manner.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Sustainable Advances in Cultural Heritage Conservation and Archaeometry)
►▼
Show Figures Francesca Caterina Izzo
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12197; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612197 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In Heritage Science, sampling is frequently performed for the subsequent diagnostics of modern and contemporary paintings using invasive analytical techniques. However, it endangers the integrity of artworks, and thus, it should be carefully planned and carried out only as a last resort by
[...] Read more.
In Heritage Science, sampling is frequently performed for the subsequent diagnostics of modern and contemporary paintings using invasive analytical techniques. However, it endangers the integrity of artworks, and thus, it should be carefully planned and carried out only as a last resort by specialists. Pigment mixtures have commonly been employed by modern and contemporary artists due to the ease of combining paints on the color palette. Hence, a painting might include both primary/secondary paints and mixtures of those. Therefore, obtaining a sample from a mixture might be sufficient for the identification of the individual primary-colored paints. This study focused on the creation of a user-friendly computational workflow for the analysis of images of paintings for the identification of mixtures using cluster analysis (K-means and Fuzzy C-means clustering). Sixteen modern and contemporary paintings that belong to the International Gallery of Modern Art Ca’ Pesaro in Venice have been selected: seven of them by Guido Cadorin (1892–1976), six by Andreina Rosa (1924–2019), and three by Boris Brollo (b. 1944), and the artworks of the latter being examined for the first time in this study (using Raman and ER–FTIR spectroscopies). It was found that mixtures can be identified in unvarnished paintings that consist of both non-overlapping and vibrant-colored paint layers, like those of Boris Brollo, and overlapping paint layers, like those of Andreina Rosa. Moreover, K-means clustering performs better in the case of non-overlapping colors, whereas Fuzzy C-means in the case of overlapping colors. In contrast, paintings that have been rendered with dark colors and that present a varnish layer, like those of Guido Cadorin, cannot be preliminary investigated in the proposed manner.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Sustainable Advances in Cultural Heritage Conservation and Archaeometry)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Role of ChatGPT and Skilled Workers for Business Sustainability: Leadership Motivation as the Moderator by Demetris Vrontis, Demetris Vrontis,  Ranjan Chaudhuri and Ranjan Chaudhuri and  Sheshadri Chatterjee
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12196; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612196 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
ChatGPT is an AI tool that was primarily developed by OpenAI with the support of its GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 platforms and large language models. ChatGPT has been fine-tuned with both supervised and reinforcement learning technology. Various types of organizations are interested in adopting
[...] Read more.
ChatGPT is an AI tool that was primarily developed by OpenAI with the support of its GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 platforms and large language models. ChatGPT has been fine-tuned with both supervised and reinforcement learning technology. Various types of organizations are interested in adopting applications supported by GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 platforms, but there is an acute shortage of trained workers in this field. Research is needed to investigate the role of this very new technology and skilled workers in maintaining business sustainability. Also, few studies have investigated the role of leadership motivation in accelerating business sustainability. Therefore, this study aims to examine the role of ChatGPT and skilled employees in business sustainability. It also investigates the moderating impact of leadership motivation on business sustainability. With the help of resource-based view (RBV) and the extant literature, a theoretical model was developed, which was then validated using the PLS-SEM technique on feedback from 209 respondents. The study finds that both ChatGPT and skilled workers have significant impact on improving business sustainability. The study also demonstrates that leadership motivation significantly impacts business sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Disruptive Innovation and Sustainable Growth)
►▼
Show Figures Sheshadri Chatterjee
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12196; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612196 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
ChatGPT is an AI tool that was primarily developed by OpenAI with the support of its GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 platforms and large language models. ChatGPT has been fine-tuned with both supervised and reinforcement learning technology. Various types of organizations are interested in adopting
[...] Read more.
ChatGPT is an AI tool that was primarily developed by OpenAI with the support of its GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 platforms and large language models. ChatGPT has been fine-tuned with both supervised and reinforcement learning technology. Various types of organizations are interested in adopting applications supported by GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 platforms, but there is an acute shortage of trained workers in this field. Research is needed to investigate the role of this very new technology and skilled workers in maintaining business sustainability. Also, few studies have investigated the role of leadership motivation in accelerating business sustainability. Therefore, this study aims to examine the role of ChatGPT and skilled employees in business sustainability. It also investigates the moderating impact of leadership motivation on business sustainability. With the help of resource-based view (RBV) and the extant literature, a theoretical model was developed, which was then validated using the PLS-SEM technique on feedback from 209 respondents. The study finds that both ChatGPT and skilled workers have significant impact on improving business sustainability. The study also demonstrates that leadership motivation significantly impacts business sustainability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Disruptive Innovation and Sustainable Growth)
►▼
Show Figures
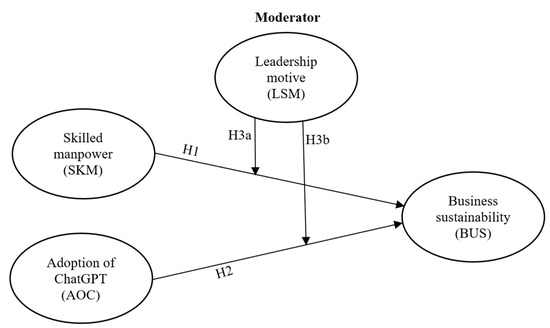 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle The Influence of Road Pavement Materials on Surface Texture and Friction by Matúš Kováč, Matúš Kováč,  Matej Brna, Matej Brna,  Peter Pisca, Peter Pisca,  Dušan Jandačka and Dušan Jandačka and  Martin Decký
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12195; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612195 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
This article’s primary goal was to analyze the effect of texture on skid resistance. Surface texture was recorded with a revolutionary device designed to create 3D surface scans, the Static Road Scanner. The skid resistance was represented by a pendulum test value. Measurements
[...] Read more.
This article’s primary goal was to analyze the effect of texture on skid resistance. Surface texture was recorded with a revolutionary device designed to create 3D surface scans, the Static Road Scanner. The skid resistance was represented by a pendulum test value. Measurements were made on three different groups of surfaces. Reference surfaces with known standard grain sizes represented the first group. The second group consisted of specimens made from a different type of aggregate. The last group of surfaces consisted of asphalt specimens made from different sizes and types of aggregates used in a mixture. The test results shed some more light on understanding texture’s effect on surface friction. Although some results were expected, not all of them were proven. For instance, a high level of texture doesn’t necessarily mean high friction. A relatively strong relationship was found between friction and microtexture on the reference surfaces with grain sizes up to 125 µm. However, the relationships between texture and skid resistance on the aggregate and asphalt specimens turned out to be shallow for the investigated samples. For this reason, it was recommended to expand the number of investigated surfaces in further research to ensure sufficiently different levels of texture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Approaches to Improving Road Traffic Safety and Environmental Capacity)
►▼
Show Figures Martin Decký
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12195; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612195 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
This article’s primary goal was to analyze the effect of texture on skid resistance. Surface texture was recorded with a revolutionary device designed to create 3D surface scans, the Static Road Scanner. The skid resistance was represented by a pendulum test value. Measurements
[...] Read more.
This article’s primary goal was to analyze the effect of texture on skid resistance. Surface texture was recorded with a revolutionary device designed to create 3D surface scans, the Static Road Scanner. The skid resistance was represented by a pendulum test value. Measurements were made on three different groups of surfaces. Reference surfaces with known standard grain sizes represented the first group. The second group consisted of specimens made from a different type of aggregate. The last group of surfaces consisted of asphalt specimens made from different sizes and types of aggregates used in a mixture. The test results shed some more light on understanding texture’s effect on surface friction. Although some results were expected, not all of them were proven. For instance, a high level of texture doesn’t necessarily mean high friction. A relatively strong relationship was found between friction and microtexture on the reference surfaces with grain sizes up to 125 µm. However, the relationships between texture and skid resistance on the aggregate and asphalt specimens turned out to be shallow for the investigated samples. For this reason, it was recommended to expand the number of investigated surfaces in further research to ensure sufficiently different levels of texture.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Approaches to Improving Road Traffic Safety and Environmental Capacity)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle How Does Green Insurance Affect Green Innovation? Evidence from China by Yucai Hu, Yucai Hu,  Shaorui Du, Shaorui Du,  Yukun Wang and Yukun Wang and  Xinya Yang
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12194; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612194 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the context of the rapid development of green finance, this paper examines the impact of green insurance on green innovation. Based on panel data of listed firms from 2008 to 2020, we find that green insurance significantly increased firms’ green patent applications.
[...] Read more.
In the context of the rapid development of green finance, this paper examines the impact of green insurance on green innovation. Based on panel data of listed firms from 2008 to 2020, we find that green insurance significantly increased firms’ green patent applications. The mechanisms driving this positive relationship between green insurance and green innovation include that the insured firms are able to obtain more resources, are more willing to take risks, and are more likely to have a long-term vision. Further analysis shows that green insurance can enhance a firm’s environmental performance by promoting green innovation. This study deepens our understanding of green insurance and enriches the research related to green finance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures Xinya Yang
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12194; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612194 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the context of the rapid development of green finance, this paper examines the impact of green insurance on green innovation. Based on panel data of listed firms from 2008 to 2020, we find that green insurance significantly increased firms’ green patent applications.
[...] Read more.
In the context of the rapid development of green finance, this paper examines the impact of green insurance on green innovation. Based on panel data of listed firms from 2008 to 2020, we find that green insurance significantly increased firms’ green patent applications. The mechanisms driving this positive relationship between green insurance and green innovation include that the insured firms are able to obtain more resources, are more willing to take risks, and are more likely to have a long-term vision. Further analysis shows that green insurance can enhance a firm’s environmental performance by promoting green innovation. This study deepens our understanding of green insurance and enriches the research related to green finance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessReview From Hype to Reality: Unveiling the Promises, Challenges and Opportunities of Blockchain in Supply Chain Systems by Muen Uddin, Muen Uddin,  Shitharth Selvarajan, Shitharth Selvarajan,  Muath Obaidat, Muath Obaidat,  Shams Ul Arfeen, Shams Ul Arfeen,  Alaa O. Khadidos, Alaa O. Khadidos,  Adil O. Khadidos and Adil O. Khadidos and  Maha Abdelhaq
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12193; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612193 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology widely adopted in industrial applications for improving supply chain management (SCM). The SCM and logistics communities have paid close attention to the development of blockchain technology. The primary purpose of employing a blockchain for SCM is to lower
[...] Read more.
Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology widely adopted in industrial applications for improving supply chain management (SCM). The SCM and logistics communities have paid close attention to the development of blockchain technology. The primary purpose of employing a blockchain for SCM is to lower production costs while enhancing the system’s security. In recent years, blockchain-related SCM research has drawn much interest, and it is fair to state that this technology is now the most promising option for delivering reliable services/goods in supply chain networks. This study uses rigorous methods to review the technical implementation aspects of SCM systems driven by Blockchain. To ensure the security of industrial applications, we primarily concentrated on developing SCM solutions with blockchain capabilities. In this study, the unique qualities of blockchain technology have been exploited to analyze the main effects of leveraging it in the SCM. Several security metrics are utilized to validate and compare the blockchain methodologies’ effectiveness in SCM. The blockchain may alter the supply chain to make it more transparent and efficient by creating a useful tool for strategic planning and enhancing connections among the customers, suppliers, and accelerators. Moreover, the performance of traditional and blockchain-enabled SCM systems is compared in this study based on the parameters of efficiency, execution time, security level, and latency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Revolutionizing Blockchain Technology for Smart and Sustainable Transportation and Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures Maha Abdelhaq
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12193; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612193 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology widely adopted in industrial applications for improving supply chain management (SCM). The SCM and logistics communities have paid close attention to the development of blockchain technology. The primary purpose of employing a blockchain for SCM is to lower
[...] Read more.
Blockchain is a groundbreaking technology widely adopted in industrial applications for improving supply chain management (SCM). The SCM and logistics communities have paid close attention to the development of blockchain technology. The primary purpose of employing a blockchain for SCM is to lower production costs while enhancing the system’s security. In recent years, blockchain-related SCM research has drawn much interest, and it is fair to state that this technology is now the most promising option for delivering reliable services/goods in supply chain networks. This study uses rigorous methods to review the technical implementation aspects of SCM systems driven by Blockchain. To ensure the security of industrial applications, we primarily concentrated on developing SCM solutions with blockchain capabilities. In this study, the unique qualities of blockchain technology have been exploited to analyze the main effects of leveraging it in the SCM. Several security metrics are utilized to validate and compare the blockchain methodologies’ effectiveness in SCM. The blockchain may alter the supply chain to make it more transparent and efficient by creating a useful tool for strategic planning and enhancing connections among the customers, suppliers, and accelerators. Moreover, the performance of traditional and blockchain-enabled SCM systems is compared in this study based on the parameters of efficiency, execution time, security level, and latency.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Revolutionizing Blockchain Technology for Smart and Sustainable Transportation and Logistics)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Integrated Lean-Green Practices and Supply Chain Sustainability for Manufacturing SMEs: A Systematic Literature Review and Research Agenda by Wilson Kosasih, Wilson Kosasih,  I Nyoman Pujawan and I Nyoman Pujawan and  Putu Dana Karningsih
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12192; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612192 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
While it is understandable that lean and green practices are mostly sensible for large companies, it is also important to bring these practices to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as they are the dominant players in various industry sectors. SMEs are part of
[...] Read more.
While it is understandable that lean and green practices are mostly sensible for large companies, it is also important to bring these practices to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as they are the dominant players in various industry sectors. SMEs are part of larger supply chains and contribute substantially to the economy, and thus perhaps there is a need for a workable model that attracts them to the lean and green practices. This study aims to find gaps in the lean-green research area that require development in future studies, especially for SMEs. This study uses an analysis of systematic literature reviews (SLR) and involves carefully selected articles from different databases or sources. This SLR was conducted in an effective and structured way using keywords entered into the search engine and found as many as 157 peer-reviewed journal articles, which were studied further using quantitative and qualitative approaches. The bibliometric analysis carried out made it possible to observe research trends on lean and green from 1996 to 2022. To find different research dimensions on lean and green topics, an in-depth evaluation was carried out on the linkage between lean, green, supply chain management, sustainability, and other management approaches. This study finds a lack of empirical research studies that comprehensively focus on investigating the impact of lean and green practices on the supply chain sustainability performance of manufacturing SMEs and involve all three aspects of the triple bottom line (3BL). Our review suggests such a robust and workable model for SMEs is not currently available. A limitation of our review is the use of keywords or “terms” to select articles, as well as the subjectivity of the researcher. Finally, we identify the research streams, criteria, findings, limitations, and enablers or challenges of 17 selected published journal papers on lean-green studies in SMEs and propose a number of research questions for future research directions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancing Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Circular Economy through Industry 4.0 Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures Putu Dana Karningsih
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12192; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612192 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
While it is understandable that lean and green practices are mostly sensible for large companies, it is also important to bring these practices to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as they are the dominant players in various industry sectors. SMEs are part of
[...] Read more.
While it is understandable that lean and green practices are mostly sensible for large companies, it is also important to bring these practices to small and medium enterprises (SMEs), as they are the dominant players in various industry sectors. SMEs are part of larger supply chains and contribute substantially to the economy, and thus perhaps there is a need for a workable model that attracts them to the lean and green practices. This study aims to find gaps in the lean-green research area that require development in future studies, especially for SMEs. This study uses an analysis of systematic literature reviews (SLR) and involves carefully selected articles from different databases or sources. This SLR was conducted in an effective and structured way using keywords entered into the search engine and found as many as 157 peer-reviewed journal articles, which were studied further using quantitative and qualitative approaches. The bibliometric analysis carried out made it possible to observe research trends on lean and green from 1996 to 2022. To find different research dimensions on lean and green topics, an in-depth evaluation was carried out on the linkage between lean, green, supply chain management, sustainability, and other management approaches. This study finds a lack of empirical research studies that comprehensively focus on investigating the impact of lean and green practices on the supply chain sustainability performance of manufacturing SMEs and involve all three aspects of the triple bottom line (3BL). Our review suggests such a robust and workable model for SMEs is not currently available. A limitation of our review is the use of keywords or “terms” to select articles, as well as the subjectivity of the researcher. Finally, we identify the research streams, criteria, findings, limitations, and enablers or challenges of 17 selected published journal papers on lean-green studies in SMEs and propose a number of research questions for future research directions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancing Sustainable Supply Chain Management and Circular Economy through Industry 4.0 Technologies)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Land-Use-Change-Induced Cooling and Precipitation Reduction in China: Insights from CMIP6 Models by Peizhi Tian, Peizhi Tian,  Binyang Jian, Binyang Jian,  Jianrui Li, Jianrui Li,  Xitian Cai, Xitian Cai,  Jiangfeng Wei and Jiangfeng Wei and  Guo Zhang
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12191; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612191 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the 21st century, the effect of land use/land cover change (LULCC) on climate has become an area of active research. To explore the effects of LULCC on temperature and precipitation in China, we used outputs from the BCC-CSM2-MR, CESM2, IPSL-CM6A-LR, and UKESM1
[...] Read more.
In the 21st century, the effect of land use/land cover change (LULCC) on climate has become an area of active research. To explore the effects of LULCC on temperature and precipitation in China, we used outputs from the BCC-CSM2-MR, CESM2, IPSL-CM6A-LR, and UKESM1 models, which participated in the Land Use Model Intercomparison Project (LUMIP) of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6). Based on these models, we identified temporal variations in precipitation and near-surface air temperature (hereinafter temperature) with and without historical land use changes and their relation with LULCC in China during 1850–2014. We then determined the significant changing period (1972–2012) and revealed the relation between the spatial distribution of historical change in vegetation cover types, precipitation, and temperature. The results showed that annual historical precipitation decreased faster (132.23 mm/(1000 a) faster), while annual historical temperature increased slower (2.70 °C/(1000 a) slower) than that without LULCC during 1850–2014. LULCC not only influenced surface properties to change local precipitation and temperature distributions and mean values, but also affected other components through atmospheric circulations due to typical monsoon characteristics in China. The relative contribution of grassland change to precipitation variation was the largest, while relatively, cropland change contributed the most to temperature variation. Our study innovatively used new model outputs from LUMIP to analyze the impacts of LULCC on precipitation and temperature, which can help to guide and improve future land use management and predictions of precipitation and temperature.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Environmental Sustainability and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures Guo Zhang
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12191; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612191 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
In the 21st century, the effect of land use/land cover change (LULCC) on climate has become an area of active research. To explore the effects of LULCC on temperature and precipitation in China, we used outputs from the BCC-CSM2-MR, CESM2, IPSL-CM6A-LR, and UKESM1
[...] Read more.
In the 21st century, the effect of land use/land cover change (LULCC) on climate has become an area of active research. To explore the effects of LULCC on temperature and precipitation in China, we used outputs from the BCC-CSM2-MR, CESM2, IPSL-CM6A-LR, and UKESM1 models, which participated in the Land Use Model Intercomparison Project (LUMIP) of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6). Based on these models, we identified temporal variations in precipitation and near-surface air temperature (hereinafter temperature) with and without historical land use changes and their relation with LULCC in China during 1850–2014. We then determined the significant changing period (1972–2012) and revealed the relation between the spatial distribution of historical change in vegetation cover types, precipitation, and temperature. The results showed that annual historical precipitation decreased faster (132.23 mm/(1000 a) faster), while annual historical temperature increased slower (2.70 °C/(1000 a) slower) than that without LULCC during 1850–2014. LULCC not only influenced surface properties to change local precipitation and temperature distributions and mean values, but also affected other components through atmospheric circulations due to typical monsoon characteristics in China. The relative contribution of grassland change to precipitation variation was the largest, while relatively, cropland change contributed the most to temperature variation. Our study innovatively used new model outputs from LUMIP to analyze the impacts of LULCC on precipitation and temperature, which can help to guide and improve future land use management and predictions of precipitation and temperature.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Environmental Sustainability and Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 get_app Open AccessArticle Preparation and Properties of High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt with a Novel Thermoplastic Rubber by Teng Wang, Teng Wang,  Zhirong Chen, Zhirong Chen,  Jinlong Hong, Jinlong Hong,  Zhen Liao, Zhen Liao,  Di Wang, Di Wang,  Dongdong Yuan, Dongdong Yuan,  Yufei Zhang and Yufei Zhang and  Augusto Cannone Falchetto
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12190; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612190 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
With the increasing demand for improved road performance and sustainable development, modified asphalt is increasingly being used in pavement construction. This study investigates the preparation and properties of a novel high-viscosity modified asphalt. Firstly, different contents of novel thermoplastic rubber (NTPR) were mixed
[...] Read more.
With the increasing demand for improved road performance and sustainable development, modified asphalt is increasingly being used in pavement construction. This study investigates the preparation and properties of a novel high-viscosity modified asphalt. Firstly, different contents of novel thermoplastic rubber (NTPR) were mixed with neat asphalt to prepare high-viscosity modified asphalt (HVA). Then, the basic physical properties containing penetration, a softening point, ductility, and viscosity were conducted. Moreover, the rheological properties of the HVA before and after aging were analyzed via a dynamic shear rheometer test and a bending beam rheometer test. Finally, the dispersity of the modifier in HVA was analyzed via fluorescence microscopy. The results show that adding the NTPR restricts the flow of asphalt to a certain extent and improves the high temperature performance of asphalt. Furthermore, the apparent viscosity of HVA with various contents increases less and is always less than 3 Pa·s. Although adding NTPR makes the asphalt brittle, the HVA can meet the requirements when the NTPR is from 6% to 11%. With the increase in the NTPR, the modifier forms a mesh structure in the asphalt, enhancing its stability. Considering the above results, HVA with 10~11% of NTPR is recommended because it has better comprehensive properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Organic Materials Used in the Construction Sector)
►▼
Show Figures Augusto Cannone Falchetto
Sustainability 2023, 15(16), 12190; https://doi.org/10.3390/su151612190 - 09 Aug 2023
Abstract
With the increasing demand for improved road performance and sustainable development, modified asphalt is increasingly being used in pavement construction. This study investigates the preparation and properties of a novel high-viscosity modified asphalt. Firstly, different contents of novel thermoplastic rubber (NTPR) were mixed
[...] Read more.
With the increasing demand for improved road performance and sustainable development, modified asphalt is increasingly being used in pavement construction. This study investigates the preparation and properties of a novel high-viscosity modified asphalt. Firstly, different contents of novel thermoplastic rubber (NTPR) were mixed with neat asphalt to prepare high-viscosity modified asphalt (HVA). Then, the basic physical properties containing penetration, a softening point, ductility, and viscosity were conducted. Moreover, the rheological properties of the HVA before and after aging were analyzed via a dynamic shear rheometer test and a bending beam rheometer test. Finally, the dispersity of the modifier in HVA was analyzed via fluorescence microscopy. The results show that adding the NTPR restricts the flow of asphalt to a certain extent and improves the high temperature performance of asphalt. Furthermore, the apparent viscosity of HVA with various contents increases less and is always less than 3 Pa·s. Although adding NTPR makes the asphalt brittle, the HVA can meet the requirements when the NTPR is from 6% to 11%. With the increase in the NTPR, the modifier forms a mesh structure in the asphalt, enhancing its stability. Considering the above results, HVA with 10~11% of NTPR is recommended because it has better comprehensive properties.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Organic Materials Used in the Construction Sector)
►▼
Show Figures
 Figure 1 More Articles... Submit to Sustainability
Review for Sustainability
Share
Journal Menu
►
▼
Journal Menu
Sustainability Home
Aims & Scope
Editorial Board
Reviewer Board
Topical Advisory Panel
Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
Topics
Sections & Collections
Article Processing Charge
Indexing & Archiving
Editor’s Choice Articles
Most Cited & Viewed
Journal Statistics
Journal History
Journal Awards
Society Collaborations
Conferences
Editorial Office
Journal Browser
►
▼
Journal Browser
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios
Current issue
Vol. 15 (2023)
Vol. 14 (2022)
Vol. 13 (2021)
Vol. 12 (2020)
Vol. 11 (2019)
Vol. 10 (2018)
Vol. 9 (2017)
Vol. 8 (2016)
Vol. 7 (2015)
Vol. 6 (2014)
Vol. 5 (2013)
Vol. 4 (2012)
Vol. 3 (2011)
Vol. 2 (2010)
Vol. 1 (2009)
Highly Accessed Articles
View More...
Latest Books
Submit to Sustainability
Review for Sustainability
Share
Journal Menu
►
▼
Journal Menu
Sustainability Home
Aims & Scope
Editorial Board
Reviewer Board
Topical Advisory Panel
Instructions for Authors
Special Issues
Topics
Sections & Collections
Article Processing Charge
Indexing & Archiving
Editor’s Choice Articles
Most Cited & Viewed
Journal Statistics
Journal History
Journal Awards
Society Collaborations
Conferences
Editorial Office
Journal Browser
►
▼
Journal Browser
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios
Current issue
Vol. 15 (2023)
Vol. 14 (2022)
Vol. 13 (2021)
Vol. 12 (2020)
Vol. 11 (2019)
Vol. 10 (2018)
Vol. 9 (2017)
Vol. 8 (2016)
Vol. 7 (2015)
Vol. 6 (2014)
Vol. 5 (2013)
Vol. 4 (2012)
Vol. 3 (2011)
Vol. 2 (2010)
Vol. 1 (2009)
Highly Accessed Articles
View More...
Latest Books
 More Books and Reprints...
E-Mail Alert
News
31 July 2023
MDPI’s 2022 Best PhD Thesis Awards in Environmental and Earth Sciences—Winners Announced
More Books and Reprints...
E-Mail Alert
News
31 July 2023
MDPI’s 2022 Best PhD Thesis Awards in Environmental and Earth Sciences—Winners Announced
 31 July 2023
MDPI’s 2022 Best Paper Awards in Environmental and Earth Sciences—Winners Announced
31 July 2023
MDPI’s 2022 Best Paper Awards in Environmental and Earth Sciences—Winners Announced
 31 July 2023
MDPI’s 2022 Young Investigator Awards in Environmental and Earth Sciences—Winners Announced
31 July 2023
MDPI’s 2022 Young Investigator Awards in Environmental and Earth Sciences—Winners Announced
 More News & Announcements...
Topics
Edit a Topic
Topic in
Agriculture, AgriEngineering, Energies, Sustainability, Water
Emerging Agricultural Engineering Sciences, Technologies, and Applications
Topic Editors: Muhammad Sultan, Yuguang Zhou, Redmond R. Shamshiri, Muhammad ImranDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Machines, Micromachines, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Symmetry, Wind
Energy Equipment and Condition Monitoring
Topic Editors: Zhifeng Xiao, Bin Huang, Lida LiaoDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Batteries, Designs, Energies, Materials, Sustainability
Materials for Energy Harvesting and Storage
Topic Editors: Xia Lu, Xueyi LuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Buildings, COVID, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Advanced Ventilation in and beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic
Topic Editors: John Z Lin, Zhaosong Fang, Sheng Zhang, Jian Liu, Yong Cheng, Chao HuanDeadline: 20 October 2023
More Topics
More News & Announcements...
Topics
Edit a Topic
Topic in
Agriculture, AgriEngineering, Energies, Sustainability, Water
Emerging Agricultural Engineering Sciences, Technologies, and Applications
Topic Editors: Muhammad Sultan, Yuguang Zhou, Redmond R. Shamshiri, Muhammad ImranDeadline: 31 August 2023
Topic in
Machines, Micromachines, Remote Sensing, Sustainability, Symmetry, Wind
Energy Equipment and Condition Monitoring
Topic Editors: Zhifeng Xiao, Bin Huang, Lida LiaoDeadline: 15 September 2023
Topic in
Batteries, Designs, Energies, Materials, Sustainability
Materials for Energy Harvesting and Storage
Topic Editors: Xia Lu, Xueyi LuDeadline: 30 September 2023
Topic in
Buildings, COVID, Energies, Environments, IJERPH, Sustainability
Advanced Ventilation in and beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic
Topic Editors: John Z Lin, Zhaosong Fang, Sheng Zhang, Jian Liu, Yong Cheng, Chao HuanDeadline: 20 October 2023
More Topics
 Conferences
Announce Your Conference
14 September 2023
The 10th World Sustainability Forum
Conferences
Announce Your Conference
14 September 2023
The 10th World Sustainability Forum 23–24 August 2023
5th International Conference on Green Environmental Engineering and Technology 2023 (IConGEET 2023)
23–24 August 2023
5th International Conference on Green Environmental Engineering and Technology 2023 (IConGEET 2023) 7–8 September 2023
4D Materials Design and Additive Manufacturing Conference 2023
7–8 September 2023
4D Materials Design and Additive Manufacturing Conference 2023 More Conferences...
Special Issues
Edit a Special Issue
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable E-learning and Education with Intelligence
Guest Editor: Hao-Chiang Koong LinDeadline: 12 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable Supply Chain Innovation and Operation Management
Guest Editors: Lei Xu, Xiaochen Sun, Guihong Zhao, Xiaohang YueDeadline: 15 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Characteristics, Health Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management of Air Pollutants in Asia
Guest Editors: Fei Li, Dingyi Wang, Hongtao YiDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Human–River Interactions in Cities
Guest Editors: G. Mathias Kondolf, Amir Gohar, Yves-François Le LayDeadline: 15 September 2023
More Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Eutrophication and Sustainable Management of Water
Collection Editor: Marco Ragazzi
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Power System and Sustainability
Collection Editors: Gaetano Zizzo, Favuzza Salvatore
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Marketing and Sustainability
Collection Editor: Colin Michael Hall
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Teacher Professional Development in ESD
Collection Editor: Michele Biasutti
More Topical Collections
Sustainability,
EISSN 2071-1050,
Published by MDPI
RSS
Content Alert
Further Information
Article Processing Charges
Pay an Invoice
Open Access Policy
Contact MDPI
Jobs at MDPI
Guidelines
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
MDPI Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
Follow MDPI
LinkedIn
Facebook
Twitter
More Conferences...
Special Issues
Edit a Special Issue
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable E-learning and Education with Intelligence
Guest Editor: Hao-Chiang Koong LinDeadline: 12 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Sustainable Supply Chain Innovation and Operation Management
Guest Editors: Lei Xu, Xiaochen Sun, Guihong Zhao, Xiaohang YueDeadline: 15 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Characteristics, Health Risk Assessment and Sustainable Management of Air Pollutants in Asia
Guest Editors: Fei Li, Dingyi Wang, Hongtao YiDeadline: 31 August 2023
Special Issue in
Sustainability
Human–River Interactions in Cities
Guest Editors: G. Mathias Kondolf, Amir Gohar, Yves-François Le LayDeadline: 15 September 2023
More Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Eutrophication and Sustainable Management of Water
Collection Editor: Marco Ragazzi
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Power System and Sustainability
Collection Editors: Gaetano Zizzo, Favuzza Salvatore
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Marketing and Sustainability
Collection Editor: Colin Michael Hall
Topical Collection in
Sustainability
Teacher Professional Development in ESD
Collection Editor: Michele Biasutti
More Topical Collections
Sustainability,
EISSN 2071-1050,
Published by MDPI
RSS
Content Alert
Further Information
Article Processing Charges
Pay an Invoice
Open Access Policy
Contact MDPI
Jobs at MDPI
Guidelines
For Authors
For Reviewers
For Editors
For Librarians
For Publishers
For Societies
For Conference Organizers
MDPI Initiatives
Sciforum
MDPI Books
Preprints.org
Scilit
SciProfiles
Encyclopedia
JAMS
Proceedings Series
Follow MDPI
LinkedIn
Facebook
Twitter
 © 1996-2023 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated
Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely
those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or
the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas,
methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
We use cookies on our website to ensure you get the best experience.
Read more about our cookies here.
Accept
Share Link
Copy
clear
Share
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/sustainability
clear
Back to TopTop
© 1996-2023 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated
Disclaimer
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely
those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or
the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas,
methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
Terms and Conditions
Privacy Policy
We use cookies on our website to ensure you get the best experience.
Read more about our cookies here.
Accept
Share Link
Copy
clear
Share
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/sustainability
clear
Back to TopTop
|
【本文地址】